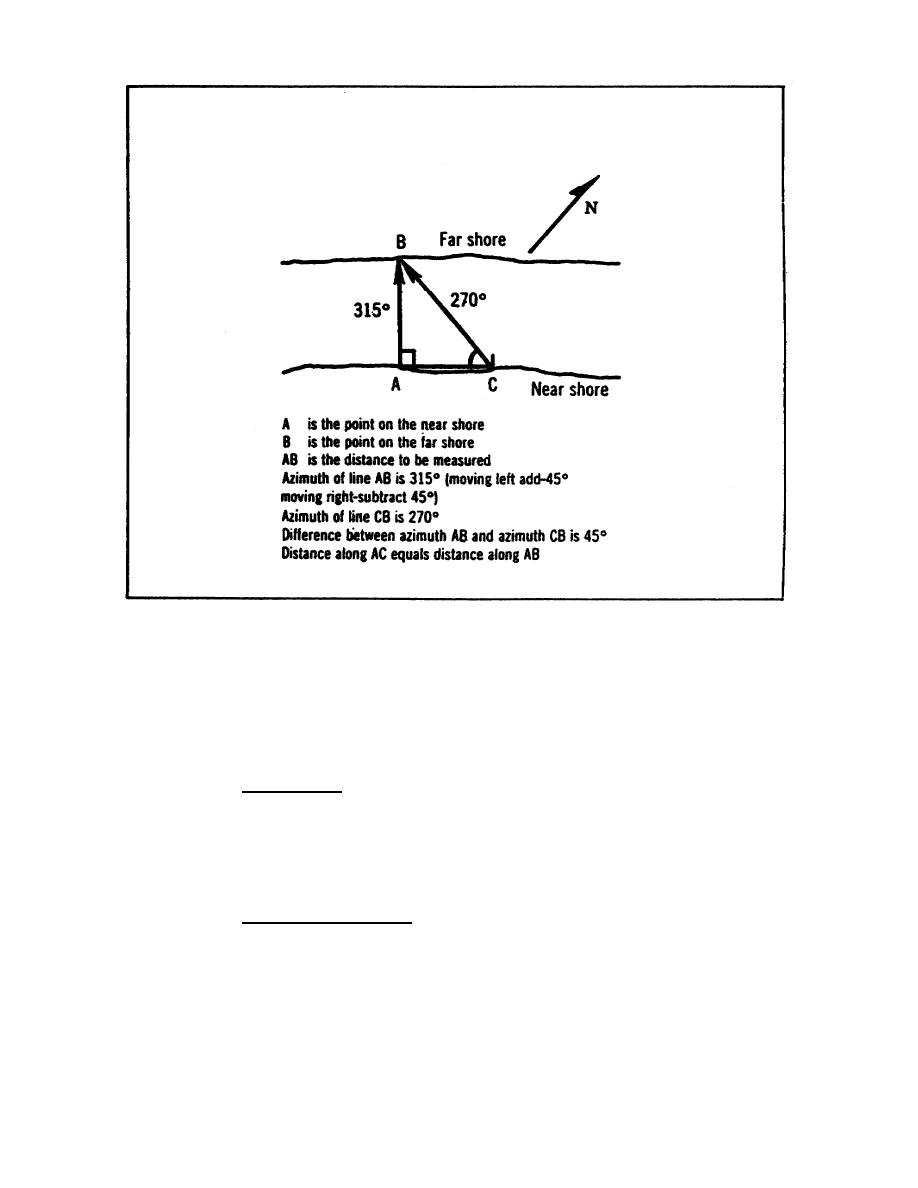
FIGURE 1-24.
MEASURING STREAM WIDTH.
distance along the bank.
Throw a light object that will float into the
stream.
Record the time required for the object to float the measured
distance. Repeat this several times and use the average time. Then divide
the measured distance by the average time in seconds.
The result is the
velocity of the stream.
(4) Approaches. You must examine the approaches to the ford on
both shores. Approaches are classified as easy or difficult. This is based
on whether the ford is to be used for personnel or vehicles.
If the
approaches, to include the slope, would require little or no improvement,
they are considered easy. If they require improvement before they can be
used, they are considered difficult.
Natural Obstacles. The bottom of the ford must be examined
to determine what kind of material it consists of. The standard types of
bottoms are listed below, with their appropriate symbol.
M-Mud
C-Clay
S-Sand
G-Gravel
R-Rock
P-Artificial Paving
1-57
MP1028



 Previous Page
Previous Page
